How to Achieve Stable Blood Pressure?
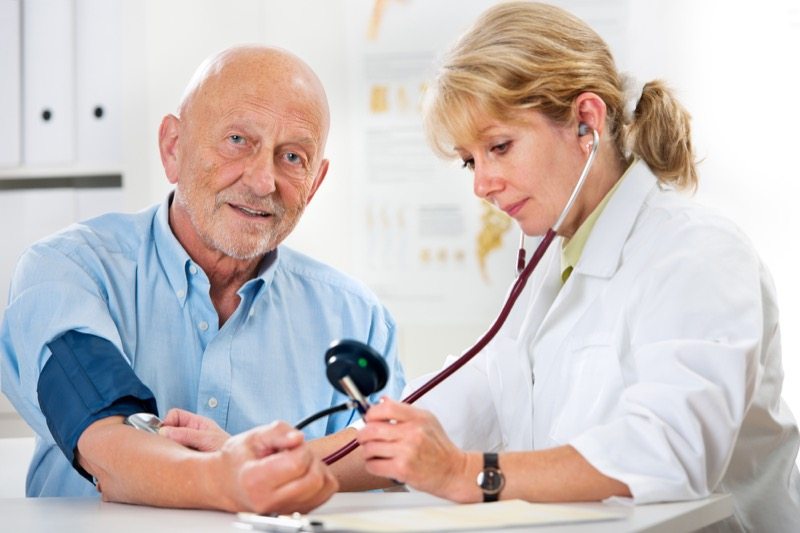 Regardless of your age, seesawing blood pressure is not a healthy sign. Indeed, it may be life-threatening. While some fluctuation in blood pressure is normal, persistent severe ups and downs can be very dangerous. The goal is stable blood pressure.
Regardless of your age, seesawing blood pressure is not a healthy sign. Indeed, it may be life-threatening. While some fluctuation in blood pressure is normal, persistent severe ups and downs can be very dangerous. The goal is stable blood pressure.
If your blood pressure ranges from 140 over 90 to 100 over 65, that’s considered normal.
At Fairview Rehab & Nursing Home we regularly measure clients’ blood pressure and advise people what they can do to improve their health. We also have trained therapists on hand to monitor your safe use of our exercise equipment. While there are dozens of blood pressure pills on the market, our doctors can advise which, if any, to take.
If you have a healthy heart, you should have stable blood pressure.
Why is stable blood pressure important?
Low blood pressure can slow the movement of blood against the pull of gravity. This means, for instance, that blood may have difficulty flowing to the brain or kidneys at the optimum rate. Blood carries oxygen and if the brain does not get enough of it, dizziness and fainting can occur. Low blood pressure can also lead to a build-up of fluids in the lower legs.
On the other hand, high blood pressure (also known as hypertension) can damage arteries, leading to strokes and heart attacks. Note that hypertension has nothing to do with anxiety – a common misconception.
Hardening of arteries
Many older people have calcium and cholesterol deposits in their arteries. This makes the arteries stiff and less flexible, eventually leading to hypertension. However, stiff arteries also cause systolic hypertension. When you take your blood pressure, the ideal gap between the upper and lower figures should be 40. If it is much greater than that, you may have systolic hypertension.
Unfortunately, there is no silver bullet to deal with this situation. Most pills either raise or lower blood pressure. They don’t regulate it.
Causes
Some of the more common causes of erratic blood pressure numbers are medication, adrenal fatigue and hardened arteries.
Adrenal fatigue is common in elderly people and leads to low blood pressure. Overactive adrenals, on the other hand, can cause a spike in blood pressure, especially if you are excited or angry. Too much caffeine, sudden exposure to very cold weather, or physical exertion can similarly cause hypertension.
Many people wrongly believe that hypertension pills regulate or stabilize blood pressure. But this is not true. Water pills, beta-blockers, and calcium channel blockers lower blood pressure when it is high. When blood pressure is already low, they do not raise it, however.
Research indicates that some medications actually prevent stable blood pressure. Anti-depressants, or pills taken for hypertension or Parkinson’s disease, quite often contribute to fluctuating blood pressure.
Lifestyle
Good lifestyle habits are key to cardiovascular health, and part of this relates to diet. For instance, a high grain, low-fat diet is bad for people with high blood pressure. And that’s a lot of people: one in three US adults are believed to have high blood pressure. Our therapists are best placed to advise you on dietary matters based on your personal circumstances.
It’s important to understand the role blood sugars play in your health. High blood sugar levels can lead to diabetes, which in turn, can increase cardiovascular problems.
The likelihood is that if you have hypertension, you may also have elevated blood sugar levels. So it’s often the case that normalizing your blood sugar levels will help you achieve a more stable blood pressure.
Similarly, high insulin levels are associated with high blood pressure. Lifestyle modifications can help reduce insulin levels and hypertension. These include losing weight through exercise, managing your emotional life and exposure to some sunshine.
Fairview has medical experts and beautiful gardens. It also offers good rehabilitation therapies to its clients, most of whom say they are relaxed and happy. It is an ideal setting in which one can achieve stable blood pressure.
This article contains informational and educational materials and does not replace health or medical advice. For questions or concerns regarding your medical condition or health objectives, speak to a qualified physician or healthcare provider.




Leave A Comment