Most Common Complications of a Humerus Fracture
The rate of healing for a humerus fracture can vary among people and depends on several factors, including the severity and location of the fracture, age, overall health, and the effectiveness of the chosen treatment. Generally, children tend to heal more quickly than adults because their bones are still growing and have a greater capacity for regeneration.
As for adults, especially older ones, healing may take longer. After the initial healing phase, physical therapy may be recommended to improve range of motion, strength, and function.
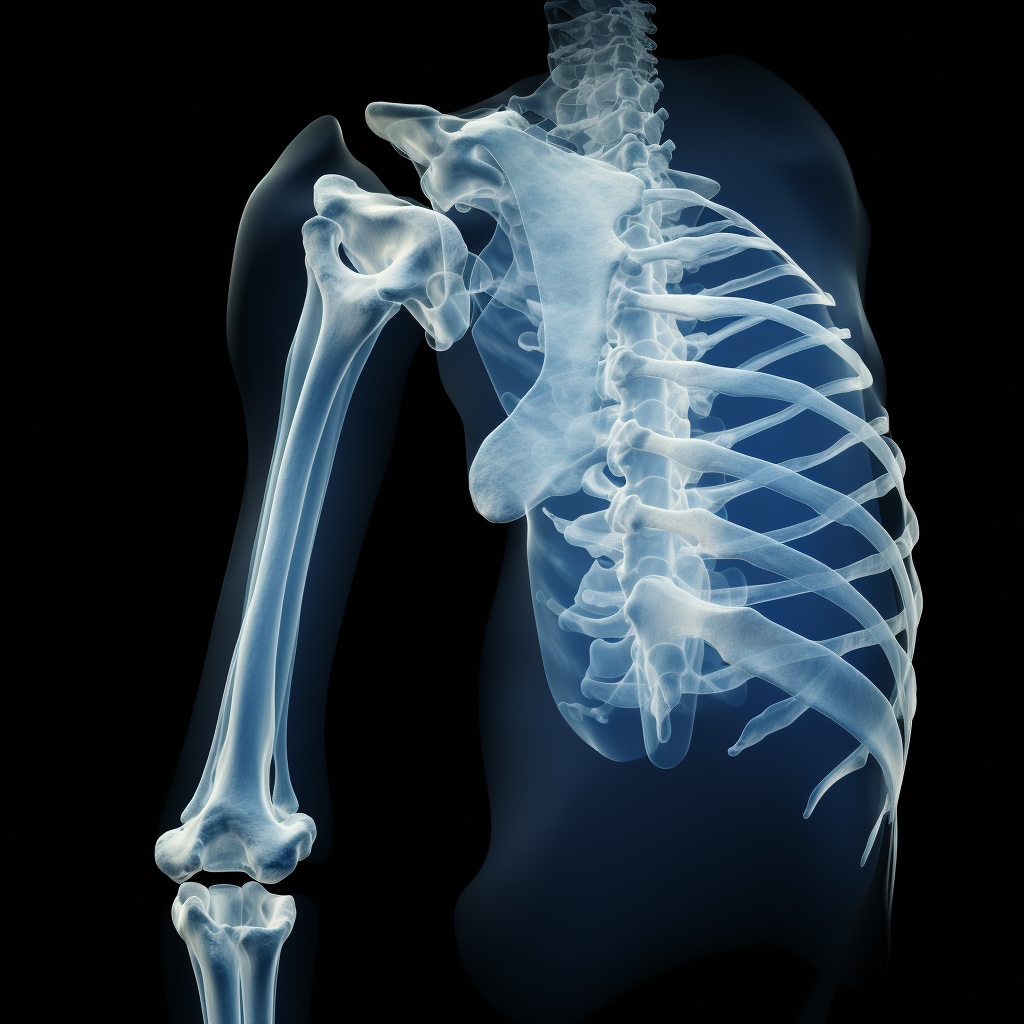
Complications of a Humerus Fracture
It’s very important to note that complications can be minimized with prompt and appropriate medical care, which may involve immobilization, surgery, and rehabilitation to restore function and strength. Individuals with a broken humerus should follow their healthcare provider’s recommendations for treatment and rehabilitation to optimize recovery and reduce the risk of complications.
- Loss of joint function
The most common complication of a broken humerus (upper arm bone) is loss of motion or function in the shoulder joint. This can occur due to various reasons, including pain, stiffness, muscle atrophy, or damage to the surrounding structures during the injury. The shoulder joint is closely associated with the humerus, and any disruption in its normal function can lead to difficulties in daily activities and reduced quality of life.
- Nerve damage
Other potential complications of a humerus fracture may include nerve or blood vessel damage, nonunion – failure of the fractured bone to heal -, malunion – improper alignment of the healed bone -, and the development of chronic pain. The specific complications can vary depending on the location and severity of the fracture, as well as the treatment approach.
- Infection
Infection can be a potential complication associated with a broken humerus, which is upper arm bone or any other fracture. Fractures, especially open fractures, where the broken bone pierces the skin, or fractures that require surgical intervention, can create a pathway for bacteria to enter the body and cause infection.
Prompt medical attention is crucial if there is suspicion of infection. In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to clean the affected area and remove any infected tissue.
What are the long-term effects of a broken humerus?
The long-term effects of a humerus fracture can vary depending on few factors, including the severity and type of the fracture, the treatment received, such as surgery involving implants and screws and the patient’s overall health. In many cases, individuals can achieve a good recovery with appropriate medical care and rehabilitation. It is important that you never leave the rehab in the middle, thinking that you already recovered. We have seen patients, whose recovery took months or even more.
Non-surgical treatment
Often non-surgical treatment is recommended for a broken humerus. Simple fracture can be treated with splinting to immobilize the arms and help healing. This is usually used for less severe humerus fractures. A sling may be used to support the arm and reduce movement during the initial healing period.
Physical therapy is used after the initial healing phase. The therapy helps to improve range of motion, strength, and function. In some cases, an external fixator, which is a device placed on the outside of the body, may be used to stabilize the fracture.
Resources:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9604576/
https://www.fracturecare.co.uk/care-plans/shoulder/proximal-humerus-fracture/shoulder-proximal-humerus/
https://www.northwell.edu/orthopaedic-institute/find-care/treatments/humerus-fracture-treatment
This article contains informational and educational materials and does not replace health or medical advice. For questions or concerns regarding your medical condition or health objectives, speak to a qualified physician or healthcare provider.





My humerus fracture involved proximal fracture n compression fracture of shaft of humerus 3 mos n I’m still having trouble. Seeing ortho this week
I broke my humorous in July of 2023 And he had surgery with a plate and screws. Ever since then my balance is off and I am having to use a Walker. Could I have
nerve damage That would cause me To be off balance